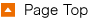Electromagnetic Actuator Technical Column: From Basics to the Latest Trends Column
Solenoid valve (Proportional control valve) complete explanation. Free fluid control's appealing points.
Hereafter, solenoid valve will be referred as proportional valve.1. Introduction
In this article, we will explain the basic mechanism, features, and structure of proportional valves. Furthermore, introduce the automation of flow control using PWM control and closed loop control.
2. What is a proportional valve?
(1) Mechanism and features
A proportional valve is a type of solenoid valve that can continuously control the flow rate and pressure of fluids through electrical signals. Unlike typical ON/OFF valves, proportional valve can easily adjust the flow rate, making it suitable for applications that require precise automatic control of fluids. Proportional control allows an efficient and flexible management of various fluids such as air, water, and oil.(2) Structure
The basic structure involves a coil, an armature, a valve body, and a spring. When the coil is energized, a magnetic field is generated and the armature shifts. The current of the coil changes the opening degree of the valve, allowing for optimal flow adjustment. The biggest feature is that the valve opening degree can be continuously changed according to the size of the electrical signal, achieving high-power flow control.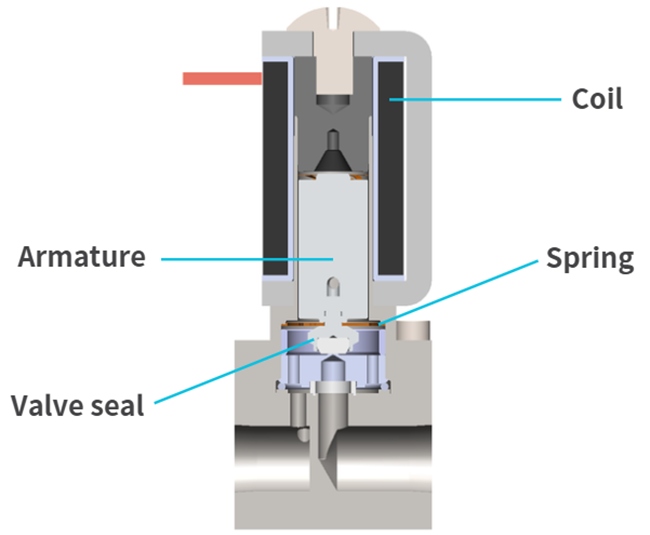
[Proportional valve structure]
(3) Compared to ON/OFF valve
Proportional valves differ significantly from ON/OFF valves. ON/OFF valves can only control two states: “open” and “close”. In contrast, proportional valves can continuously adjust the opening degree according to changes in electrical signals, allowing for fine control of flow and pressure. Compared to ON/OFF valves, which primarily perform switching functions, proportional valves possess adjustment functions, leading to major different applications and scopes of use.| ON/OFF valve | Proportional valve | |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Fluid shutoff | Flow and pressure control |
| Opening degree | 0 or 100 | Variable between 0 to 100 |
| Shut-off performance | High | Low |
| Control method | Switching drive | PWM control |

[Example: Fire adjustment]
In a household stove, the gas amount is manually controlled by turning the gas tap, but when electrified, the heat adjustment can be automated by using a proportional valve.
3. Methods of controlling a proportional valve
(1) About PWM control
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control is often used for proportional valves. This control method intermittently switches the voltage supplied to the coil of the proportional valve (coil voltage) and adjusts the on-time width (Ton) of the pulses, allowing precise control of the valve's opening and closing states. By using PWM control, the valve opening can be adjusted in proportion to the duty ratio (Ton/(Ton+Toff)), enabling precise fluid flow control. Additionally, it is compatible with various fluids such as air, gas, water, and oil, making it widely used in many industrial fields.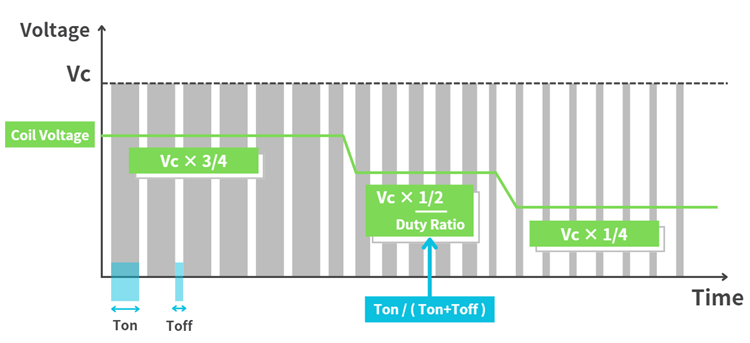
[Duty ratio and Coil voltage relationship]
(2) Automation of flow control by closed loop control
Proportional valves enable even higher precision flow control by adopting a closed-loop control system. Closed-loop control is a method that automatically adjusts control signals based on feedback from flow or pressure sensors. This control function adjusts the flow rate and pressure to be constantly maintained at the set values.For instance, if the flow rate of fluid passing through the valve exceeds a certain set point, the control system automatically restricts the valve opening to adjust the flow. However, if the flow rate is less than the set value, the opening is adjusted to expand. This process occurs in real-time, allowing a quick response to changes in external conditions and usage situations.
This closed-loop control is particularly effective in fields where precise flow management is required, such as combustion gas adjustments, supply of dried compressed air or oxidation prevention using nitrogen gas. Furthermore, combining it with PWM control enables high efficiency and accurate fluid control, finding wide application in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, medical and analytical instruments, automotive, and food industries.
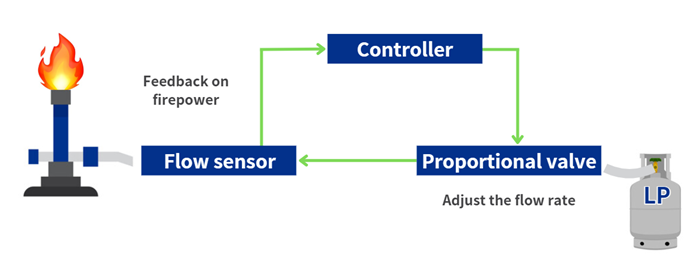
[Example: Fire adjustment]
For more information about Takano's proportional valve specifications, click the link below.
Takano's proportional valve supports PWM control.
For more information about Takano's PWM control dedicated controller for proportional valves, click the link below.
By combining your flow sensor with a dedicated proportional valve controller, you can easily create an automatic flow control environment with closed-loop control.
4. Summary
This time, we explained the mechanisms, features, and structure of proportional valves, introducing precise flow control using PWM control and closed-loop control. We hope this will be of some assist when considering valves and operations. If you have any concerns or requests for more detailed information, please feel free to contact us at any time.