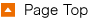Electromagnetic Actuator Technical Column: From Basics to Latest Trends
Column
A detailed comparison on Optical Shutters! Slide Type VS Rotary Type
2. What Is an Optical Shutter?
3. Comparison on Slide-Type and Rotary-Type Shutters
4. Features of Rotary Solenoid-Type Shutters
1. Introduction
This column offers a detailed overview of the types and operating principles of "optical shutters," commonly used in devices like infrared cameras, laser processing systems, and precision measuring equipment.
It specifically compares the structures and features of two main types—the "slide type" and the "rotary type"—while highlighting their applications and essential selection considerations.
We aim for this information to serve as a useful resource for individuals exploring the adoption of optical shutters, helping you make the best possible choice.
2. What Is an Optical Shutter?
Optical shutters are critical components in optical and precision measuring instruments, regulating the passage and blockage of light. Through mechanical operation, they perform the essential role of allowing or interrupting light at the required timing.
For example, in infrared cameras that use the bolometer method (thermal detection type), shutters are essential for capturing reference images to address pixel sensitivity variations and temperature fluctuation, known as NUC correction (Non-Uniformity Correction). The quality and durability of the shutter used in this correction process significantly influence the camera's overall image quality and measurement accuracy.
3. Comparison on Slide-Type and Rotary-Type Shutters
Slide shutters and rotary shutters each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Please select the one that best suits your intended use.
| Slide Shutters | Rotary Shutters | |
|---|---|---|

|

|
|
| Operation | Shutter plate slides | Shutter plate rotates at a specific angle |
| Sliding movement | During sliding, the shutter plate moves along the rail section while remaining in contact | There is no sliding (friction-producing contact points) of the shutter plate |
| Durability | 100,000 cycles (counted as one instance per open/close) | 5,000,000 cycles (counted as one instance per round trip) |
| Opening and closing accuracy | There is no risk of misalignment in the position of the shutter plate | There is a risk of misalignment in the rotational angle position |
| Design | Since the shape of the opening is fixed, the design flexibility is limited | The shape of the shutter plate offers a high degree of flexibility |
| Price | Generally inexpensive Motor-driven types are expensive |
Slightly expensive |
4. Features of Rotary Solenoid-Type Shutters
Takano offers a wide range of rotary shutters utilizing rotary solenoids for their drive actuators.
Our products stand out for their compact size, durability, and exceptional design adaptability.
① Compact and High Torque
Our ultra-compact rotary shutters, among the smallest in the industry, provide sufficient torque to operate large shutters.
Their space-saving design allows for installation in confined areas, enhancing equipment compactness.
② High Durability Clearing 5 Million Cycles
With a unique structure where the shutter plate is directly mounted on the rotation shaft supported by bearings, our shutters eliminate sliding components that typically cause wear.
This design minimizes wear-related issues, ensuring long service life and reliability.
③ Advanced Design Flexibility
The positioning of actuators and the aperture shape of the shutters can be customized to suit operational requirements. This enables the construction of an optimal layout tailored to design requirements, contributing to improved design flexibility for your equipment.
5. Application Cases of Rotary-Type Shutters
①Sensor Calibration
Example: Infrared Camera
What is an infrared camera?
An infrared camera is a device that utilizes infrared radiation to visualize the temperature distribution of objects.
Operating with wavelengths beyond the visible spectrum, it detects heat (infrared radiation) emitted by objects and converts it into an infrared image, making heat patterns visible despite being invisible to the human eye.
① Calibration Timing
The rotary shutter functions either at set intervals or in response to specific conditions, such as changes in temperature.
For instance, when there is a sudden shift in ambient temperature or after a predetermined duration, the shutter closes, initiating the calibration process.
② Function of the Shutter
During shutter closure, the sensor is isolated from external infrared radiation and light, detecting only its internally generated thermal or electronic noise.
This allows the acquisition of internal reference signals (offset) necessary for accurate measurements.
③ Shutter Reopening and Cyclical Operation
After completing calibration, the shutter reopens, enabling the sensor to resume detecting external infrared radiation. By repeatedly and automatically cycling through this operation, the sensor ensures consistent accuracy in temperature measurements over extended periods.
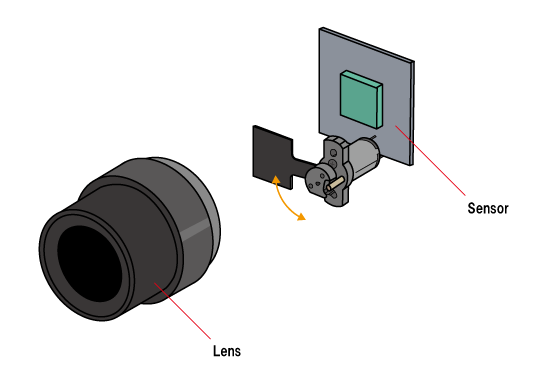
②Light Shielding
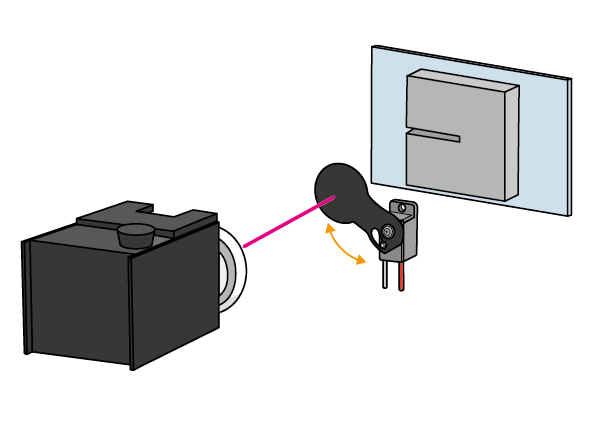
Example: Laser Processing Machine・Laser Marking
① High-Speed Mechanical Shutter for Addressing Delays in Light Source Responsiveness
Laser processing machines often require an immediate light-blocking mechanism to maintain precision.
When the on/off speed of the light source is slow, mismatched processing timing occurs, making precise processing difficult. To address this, high-speed rotary shutters are employed to control the transmission and blocking of light with precise timing.
This allows for stringent regulation of laser irradiation timing, enhancing processing accuracy and precision.
② Magnetic Recovery Model as a Fail-Safe Mechanism for Emergency Shutdowns
Safety measures demand the ability to quickly shut off the light source in emergency situations. The magnetic recovery model of optical shutters uses permanent magnets to automatically engage recovery operations when power is lost. This fail-safe mechanism ensures the light source is swiftly shut down during power outages or unexpected malfunctions, safeguarding both equipment and personnel.
6. Summary
In this column, we compared the characteristics of slide shutters and rotary shutters and introduced the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Both methods have unique features, and proper selection according to application and design conditions is essential.
We hope this column serves as a helpful reference for those considering the introduction and operation of optical shutters. At Takano, we provide both slide and rotary shutters in our product lineup and offer customization options tailored to your needs.
If you have any inquiries or wish to learn more about our products, please don't hesitate to reach out to us.
7. Contact and Information
Takano's shutter solenoid for optical devices features:
- Compact design among the smallest in the industry
- Capable of opening and closing the shutter in under 20ms
- Low power consumption
If you are considering our product, please view the details via the link below or feel free to contact us.